
At a small scale, the surface is varied and made up of small, sparkly frost deposits at the tips of high spots, surrounded by a low-lying, smooth blanket of dark material.
Prominent surface features include multi-ring structures, variously shaped impact craters, and chains of craters ( catenae) and associated scarps, ridges and deposits. It does not show any signatures of subsurface processes such as plate tectonics or volcanism, with no signs that geological activity in general has ever occurred, and is thought to have evolved predominantly under the influence of impacts. Its surface is completely covered with impact craters. The surface of Callisto is the oldest and most heavily cratered in the Solar System. Investigation by the Galileo spacecraft revealed that Callisto may have a small silicate core and possibly a subsurface ocean of liquid water at depths greater than 100 km. Compounds detected spectroscopically on the surface include water ice, carbon dioxide, silicates, and organic compounds. Ĭallisto is composed of approximately equal amounts of rock and ices, with a density of about 1.83 g/cm 3, the lowest density and surface gravity of Jupiter's major moons. It is less affected by Jupiter's magnetosphere than the other inner satellites because of its more remote orbit, located just outside Jupiter's main radiation belt. Because of this, there is a sub-Jovian point on Callisto's surface, from which Jupiter would appear to hang directly overhead. Callisto's rotation is tidally locked to its orbit around Jupiter, so that the same hemisphere always faces inward. It is not in an orbital resonance like the three other Galilean satellites- Io, Europa, and Ganymede-and is thus not appreciably tidally heated. It is the fourth Galilean moon of Jupiter by distance, with an orbital radius of about 1 883 000 km. With a diameter of 4821 km, Callisto is about 99% the diameter of the planet Mercury, but only about a third of its mass. Callisto was discovered in 1610 by Galileo Galilei. It is the third-largest moon in the Solar System after Ganymede and Saturn's largest moon Titan, and the largest object in the Solar System that may not be properly differentiated. If the above steps do not solve the issue then please send me a picture of the black brightness slider and I will look into it for further troubleshooting.Callisto ( / k ə ˈ l ɪ s t oʊ/), or Jupiter IV, is the second-largest moon of Jupiter, after Ganymede.
Windows 10 brightness slider surface update#
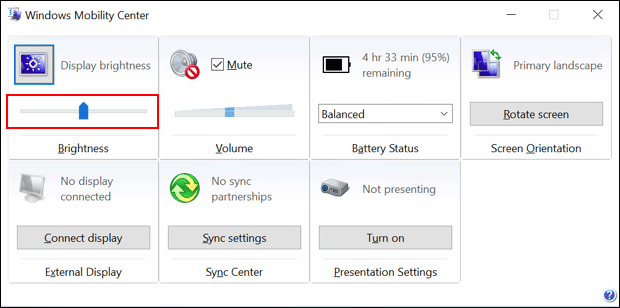
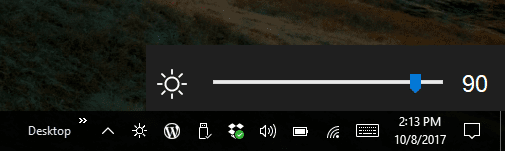
Here's how: Select the Start button, enter (type) Device Manager, select Device Manager from the list of results, expand Display adapters, right-click (or press and hold) the name of the driver (each manufacturer has a different name), and then select Update Driver Software. Note: If you don't see the slider, or if moving the slider doesn't change the brightness, try updating your display driver. Select Start, enter Display, select Display settings from the list of results, and then use the slider or turn the automatic adjustment on or off. I recommend you to perform the following steps and check if the brightness slider disappears:

I understand that there is a black brightness slider on the op left of the screen and you are unable to drag it or close it.

I came across your post and would like to help. Business PCs, Workstations and Point of Sale Systems.Printer Wireless, Networking & Internet.DesignJet, Large Format Printers & Digital Press.Printing Errors or Lights & Stuck Print Jobs.
Windows 10 brightness slider surface upgrade#


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
